
IT
is a fast-changing industry. Cloud computing has been developing rapidly in recent years and has become the foundation of a wide range of major applications, What is Cloud Computing then? Here is a Quick article of the main points as a first Chapter from the series.
Key topics:
- What is Cloud Computing
- History of Cloud Computing
- Use cases of Cloud Computing
- Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Do you know that you might already be using cloud computing, Do you know that Google Translate, your phone's backup/ restore service app, etc... and too many other apps already use cloud computing in your phone.
Advantages of cloud computing:
- On-demand Self Service
- Broad Network Access
- Resource pooling (multiple types: computing, network, & storage resource pooling)
- Rapid Elasticity (Easy to configure cloud service)
- Measured Service (Accurate & Reliable measurement)
So now,
What is Cloud Computing?
According to NIST, cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
The CLOUD word is a metaphor for the internet, while COMPUTING refers to the services provided by a sufficiently powerful computer that is capable of providing efficiency and resources and combined together with high capacity and efficient storage, and It's measurable computing service on the internet.
History of Cloud Computing
When talking about cloud computing history, we need a lot of paragraphs just for the details, So, I preferred embedding a small and clear video to show you the brief history.
(History of Cloud Computing, Utterly Amazing - The Web Series)
A brief history:
- Parallel Computing: cut a single problem into smaller parts so each part process the instruction and execute it simultaneously, thus it saves time and cost
- Distributed Computing: rare resource can be shared
- Grid Computing
- Cloud Computing
- Version 1.0
- Virtualization (What we focused on in this series)
- Higher Resource Utilization
Examples: Hyper-V, Xen, Vmware, and KVM
- Version 2.0
- Cloud-Based infrastructure
- Standardization and automation of resource utilization
Examples: Open Stack, Vmware, AWS
- Version 3.0
- Cloud-Native applications
- Agile application development & Lifecycle management
Examples: Docker, Core OS, Cloud Foundry
Cloud computing Models:
- Cloud Deployment Model
- Cloud Service Model
Cloud Deployment Models:
- Public Cloud
- widely known
- built by Cloud Service Providers
- Hybrid Cloud
- flexible
- uses corporate firewalls to isolate public & private clouds.
- Private Cloud
- Deployed and can be accessed inside the enterprise & the unit.
- How to access? you need to access the firewall which is deployed in the data center.
- Guarantee Data Security
- Industry Cloud
- A cloud platform that loads the industry or within a certain region
- contain industry features from the creation
Cloud Service Models
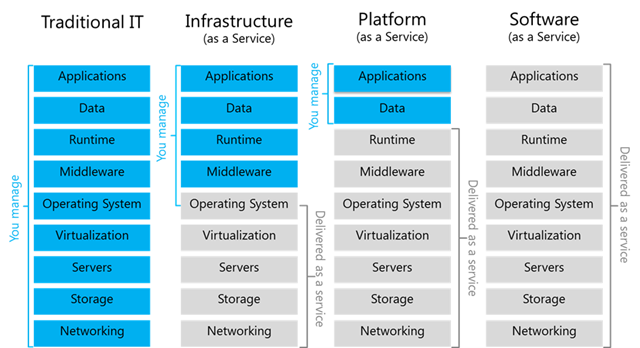
Cloud computing is obtainable in three different service models which each satisfy a singular set of business requirements. These three models are known as Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
Cloud computing has been around for quite some time now, but it will continue to grow as faster and more reliable networks offer increased benefits to service providers and consumers alike. With these advances, there are growing opportunities in an increasingly connected economy to build business models.

No comments:
Post a Comment